Peanut, also called groundnut, is a widely appreciated legume that can be cultivated on all continents. It is valued for its unique taste but also its nutritional values. Rich in energy, peanuts also contain a great amount of monosaturated acid and proteins that are essential for good health. They are a source of vitamin E and minerals. However, nutritional diversity is not the only advantage of consuming peanuts. They can be processed in various shapes and by-products to satisfy anybody’s preference.
In the Western world:
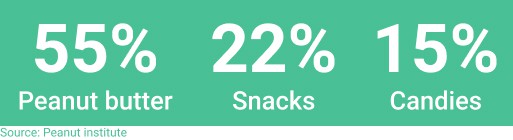
- Peanut butter is, for some, the ultimate comfort food;
- Roasted & salted peanuts are a staple snack when watching baseball games;
- Candy bars containing peanuts are consumed daily at breakfast or during the day.
In Asia and Africa:
- Peanut oil is an essential ingredient for daily cuisine as a frying oil or a dressing;
- Peanut flour is used as a source of proteins for baking or to prepare sauces like the famous saté.
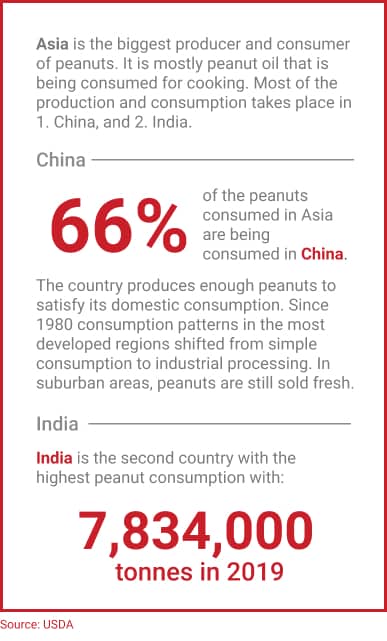
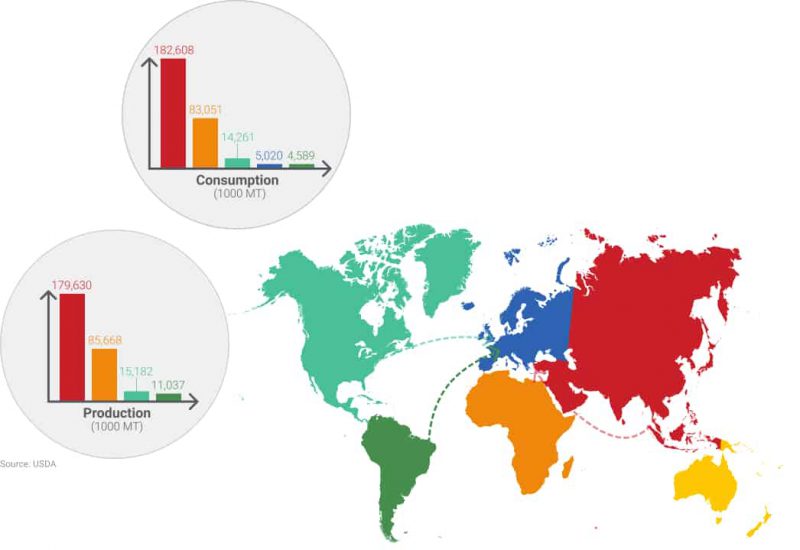
Asia: World's #1


Europe: Consumer & largest importer
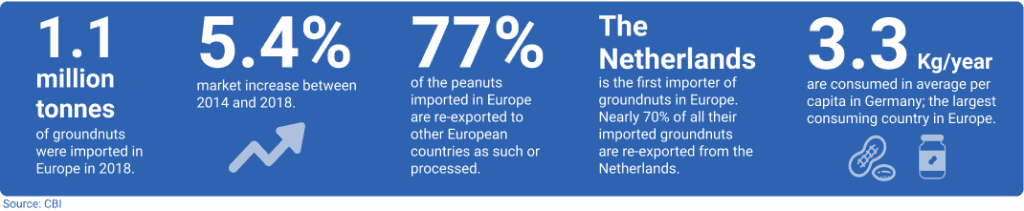

Europe is a specific market compared to Asia, America or Africa. It imports peanuts but doesn’t produce it on a scale large enough to satisfy its consumption. Because of high aflatoxin standards, Europe mainly imports from the American continent: first Argentina, and then the USA and Brazil are the main providers.
In all European countries, for the past years, imports have been increasing in terms of volume and value. Most of the products arrive in-shell or shelled but unprocessed. Value is added in Europe through transformation, for instance, in peanut butter or candy bars. That is why many products are re-exported and there is a relatively large internal European market.
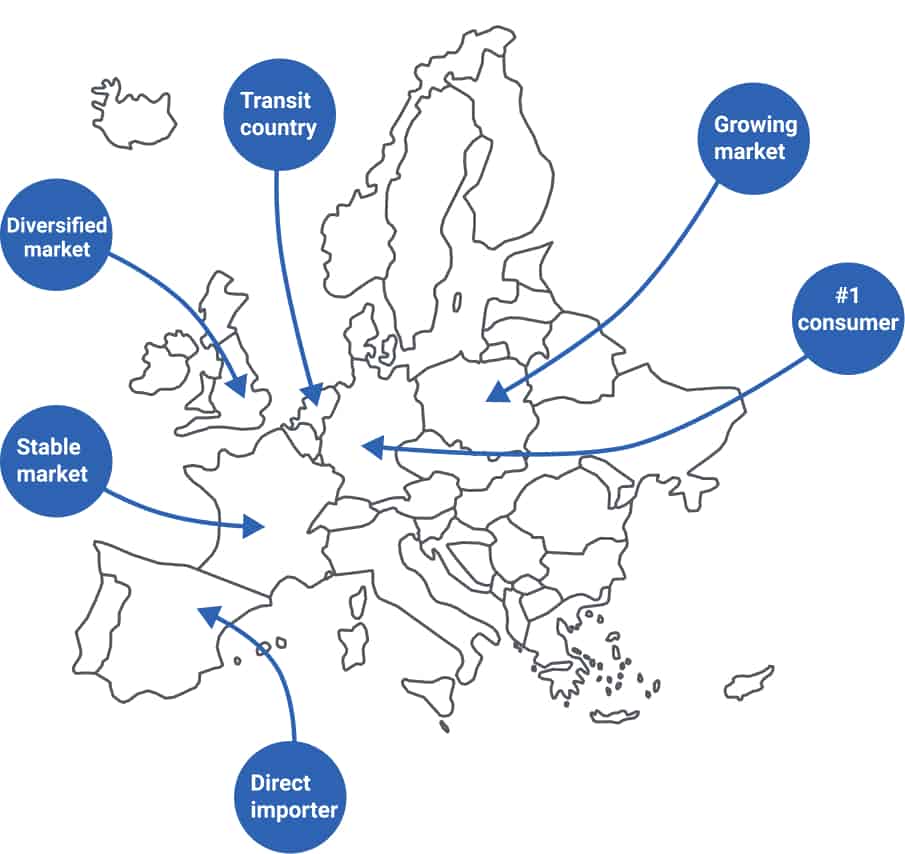
The Netherlands: a transit country
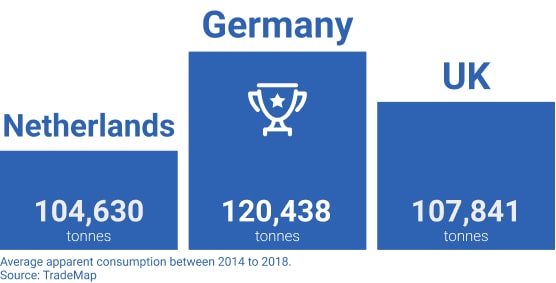
Most of the peanuts consumed in Europe transit through the port of Rotterdam. Some products are re-exported as they arrive but part of the goods are being transformed. The Netherlands is also the first European producer of peanut butter and the 3rd largest consumer of groundnuts. Dutch consumers are fond of peanut butter to spread on their famous sandwiches!
Germany: The First consumer
Large importer of groundnuts, most of them are consumed within the country. Only 30% are re-exported, compared to 70% in the Netherlands. Germans appear to be the biggest consumers with a positive balance of 120,438 tonnes between imports and (re-)exports of peanut products.
United Kingdom: a diversified market
Many small players, that is what characterises the British peanut market. The country counts many different processers and packers that develop their own brands. Peanut butter and snacks are the most appreciated products.
France: a stable market
On the contrary to the UK, France counts a relatively small number of players which mostly imports peanuts from the Netherlands. It is the 4th consumer and importer of peanuts in Europe.
Spain: a direct importer
Spain markets differ from other European countries and imports as it imports most of its peanuts directly from China. Just like France, the market has been relatively stable in the past years.
Poland: a growing market
Recently, this country has seen the highest growth with an increase of 11% of the volume imported between 2014 and 2018. It is also an increasingly important reseller as 40% of the volume is re-exported to other countries.
America: the heart of the peanut chain
North America
During the World Peanut Meeting, held in July 2020, Bob Parker, from the National Peanut Board, mentioned: “Peanut butter is the ultimate American comfort food”.
This describes the extent to which American consumers enjoy peanut and its by-products.
Highly appreciated for their nutritional values in a country where many children and adults suffer from malnutrition and obesity; peanuts are the most popular nut choice. It is considered to be an affordable source of protein.

The United States is also amongst the biggest producers of peanuts. Production is used for domestic consumption but also exports to Europe and Asia.
South America
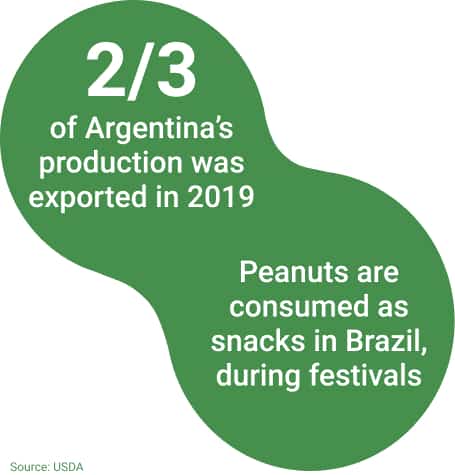
South America is the 4th producer of peanuts but the 5th consumer. The main producing countries are Argentina and Brazil. The specificity of the Argentinian peanut market is that domestic consumption is very low and most of the ground-nuts are exported.
Argentina is the main origin of peanuts exported to Europe. Brazil, on the other hand, consumes about half of the production.

 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. For more information, please read our
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. For more information, please read our